The normal period of residency at WPI is 16 terms. In addition to WPI requirements applicable to all students, students wishing to receive the major designated “Electrical and Computer Engineering” must satisfy certain distribution requirements. These requirements apply to 10 units of study in the areas of mathematics, basic science, and engineering science and design as follows:
Program Distribution Requirements for the Electrical and Computer Engineering Major
Mathematics and Basic Science (Minimum 12/3 Units)
To succeed in the study of electrical and computer engineering, the necessary foundation far exceeds what can be taught in a few introductory courses. In fact, if you even want to begin to understand what your ECE professors are talking about in lecture, you must begin with a firm basis in mathematics and the natural sciences. Moreover, whether applied to ECE or not, proficiency in mathematics and the sciences is a necessary quality for any educated engineer. Consequently, the ECE major requires a total of 4 units (12 courses) as the “Mathematics and Basic Science” distribution requirement.
The first part of this requirement is sufficient education in mathematics. At least 7 of the 12 required courses must be in this area, including coursework in differential calculus, integral calculus, differential equations, and probability. To see which specific courses fulfill these math requirements, please consult the mathematics course descriptions, and your academic advisor.
The other part of the requirement is coursework in the sciences. A solid understanding of physics is essential to any ECE student, being ultimately necessary for describing the behavior of electricity and magnetism as well as other physical phenomena. Knowledge of chemistry is useful as well, encompassing such topics as atomic and molecular behavior and the chemical properties of materials (such as silicon, which is quite useful in ECE). In recent years, knowledge of biology has also become important to electrical and computer engineers, particularly as biomedical-electrical technologies such as medical imaging continue to advance.
The ECE major requires at least 3 courses in the sciences, 2 of these courses must be in physics, and the remaining course may be in chemistry or biology depending on preference.
Finally, note that the total prescribed mathematics and science courses add up to 3 1/3 units (10 courses). To meet the distribution requirement, you then must take at least 2 more courses in any area of mathematics or science (that is, any other course with the prefix “MA”, “PH”, “CH”, “BB”, or “GE”).
Must include at least 7/3 units of math (prefix MA). Mathematics must include differential and integral calculus, differential equations, and probability.
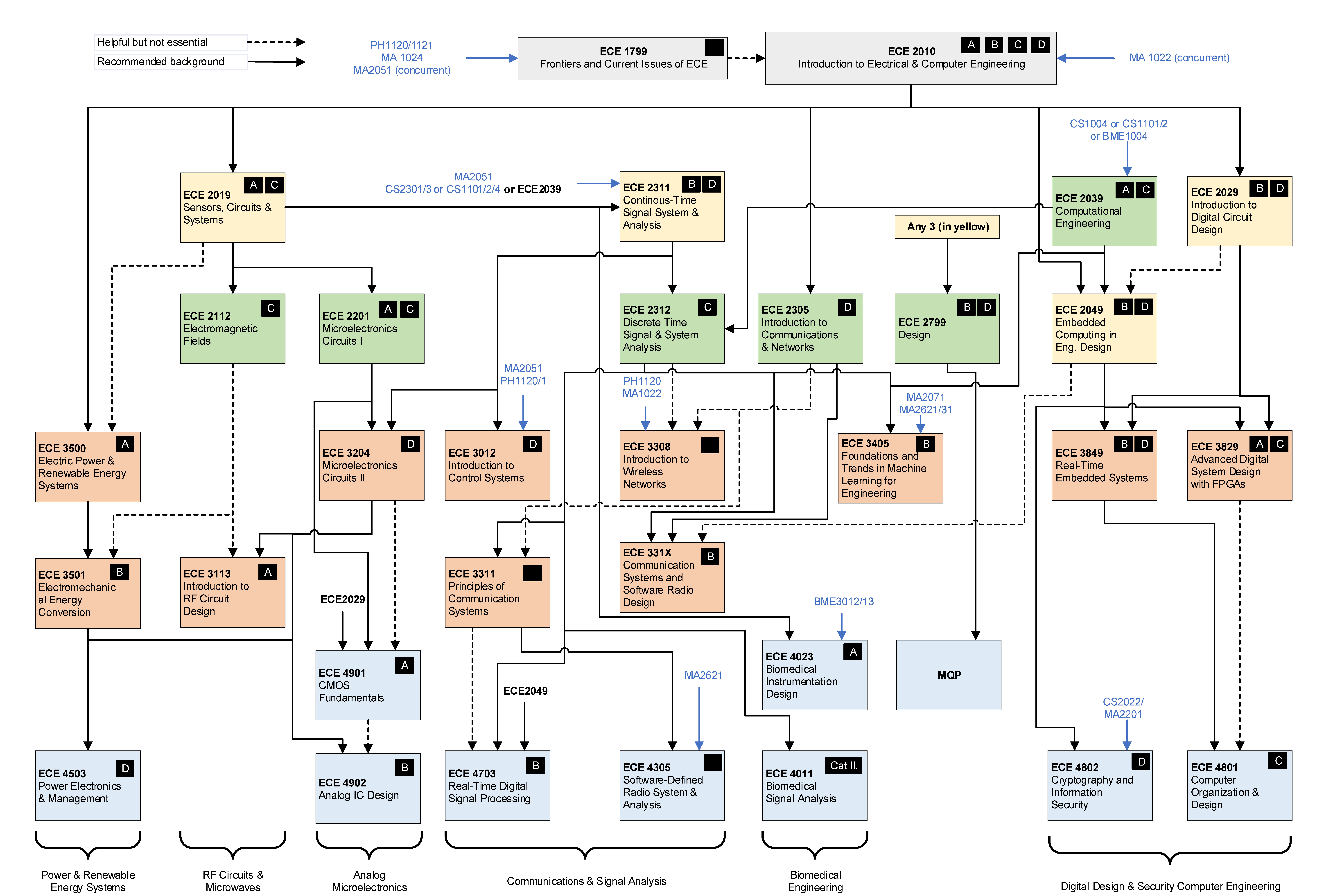
Must include at least 5 units at the 2000-level or higher within Electrical and Computer Engineering (ECE), including the MQP. Eligible courses consist of all 2000-level and higher courses with an ECE prefix and ES 3011.
The ECE course units must include at least 1 unit of courses from these approved Electrical Engineering courses:
The ECE course units must include at least 1/3 unit of Computer Engineering courses with topics in digital circuit design, satisfied by any of:
The ECE course units must include at least 1/3 unit of Computer Engineering coures with topics in embedded computing, satisfied by any of:
The ECE course units must include 1/3 unit of Capstone Design Experience. (This requirement is typically fulfilled by the MQP.)
Other Engineering Science and Design Requirements
Must include an additional 1/3 unit of computational engineering, satisfied by ECE 2039 (preferably) or by any 2000-level or above CS course except CS 2011, CS 2022, CS 3043/SS 3043.
Must include an additional 2/3 unit of engineering science and design at the 2000-level or above, selected from courses having the prefix AE, AREN, BME, CE, CHE, CS (other than CS 2011, CS 2022, CS 3043/SS 3043), ECE, ES, FP, ME, or RBE.
The above Engineering Science and Design course units must incorporate 1/3 unit of Engineering Design by either: 1) including ECE 2799 within the “Electrical and Computer Engineering Courses” (preferred option) or 2) including one of the following courses within “Other Engineering Science and Design (ES/D) Requirements”: BME 3300, CS 3733, ES 3501, ME 2300, ME 4320.
Subdisciplines Within ECE
Given a solid foundation, the MQP will allow you to demonstrate an in-depth understanding of one or more of the subdisciplines that compose the field of electrical and computer engineering. As a guide to the areas of study that can be investigated in an MQP, the ECE Course Flowchart identifies seven subdisciplines as possible areas for in-depth study leading to an MQP. Note that students should not feel constrained by these area designations — this is only one of many possible ways to organize the diverse field of electrical and computer engineering. Many if not most MQPs will incorporate subject matter from several different subdisciplines. The purpose of this list is to guide students interested in a particular area to coursework within a subdiscipline (Area Courses), relevant courses to choose from outside the subdiscipline (Related Courses), and faculty whose research and MQP advising interests fall within the subdiscipline (Area Consultants).